-
Description
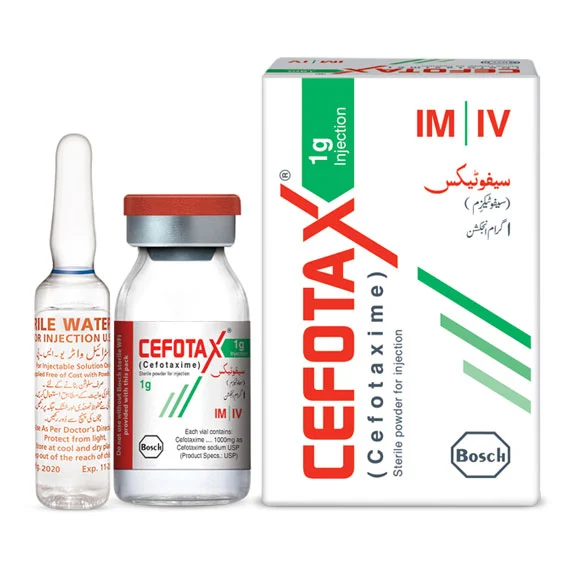
Cefotaxime 1G injection is a broad-spectrum cephalosporin antibiotic used to treat a wide range of bacterial infections. It works by inhibiting bacterial cell wall synthesis, which leads to the destruction of bacteria. Cefotaxime is effective against both Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria, making it useful for treating infections such as pneumonia, urinary tract infections, septicemia, and skin infections. It is commonly used in hospital settings, particularly for serious infections, including those involving the respiratory tract, kidneys, and bloodstream. The injection is typically administered intravenously or intramuscularly by a healthcare provider, and the dosage depends on the type and severity of the infection being treated. Cefotaxime is often used when other antibiotics may not be effective or when a broad-spectrum treatment is needed.
-
Ingredients
Cefotaxime 1G
-
Drug Class
antibiotic
-
Dosage Form
injection
-
Uses
Following are the uses of Cefotaxime 1G injection:
- Used to treat a variety of bacterial infections, including respiratory tract infections such as pneumonia and bronchitis.
- Effective in managing urinary tract infections (UTIs), including pyelonephritis and cystitis, caused by susceptible bacteria.
- Prescribed for intra-abdominal infections, including peritonitis and abscesses.
- Helps treat skin and soft tissue infections, such as cellulitis and wound infections.
- Used in the treatment of bone and joint infections like osteomyelitis and septic arthritis.
- Can be used for gynecological infections, including pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) and endometritis.
- Effective in treating bloodstream infections (bacteremia) and sepsis caused by susceptible organisms.
- Often used for treating meningitis and infections of the central nervous system.
- Commonly used in hospital settings for serious infections, particularly in immunocompromised patients or those who are critically ill.
-
Dosage
Following are the doses for Cefotaxime 1G injection:
- The typical adult dose is 1g every 12 hours for moderate infections.
- For severe infections, the dose may be increased to 2g every 12 hours.
- In life-threatening infections, such as sepsis or meningitis, the dose may be increased to 2g every 8 hours.
- The maximum recommended dose for adults is 12g per day, divided into 3 to 4 doses.
- For pediatric patients, the dose is generally 50 to 100mg per kg of body weight per day, divided into 2 to 4 doses, depending on the severity of the infection.
- In patients with renal impairment, dose adjustments may be necessary based on creatinine clearance.
-
In case of Overdose
In case of an overdose of Cefotaxime 1G injection, it is important to seek immediate medical attention. Symptoms of an overdose may include severe gastrointestinal issues, such as nausea, vomiting, or diarrhea, and in more severe cases, kidney or liver damage. Treatment will typically involve supportive care, including monitoring vital signs, fluid management, and correction of any electrolyte imbalances. In some cases, hemodialysis may be recommended to help remove the drug from the bloodstream, especially in patients with renal impairment. Do not attempt to self-treat an overdose, and contact a healthcare provider or poison control center immediately for proper management.
-
Missed Dose
If you miss a dose of Cefotaxime 1G injection, contact your healthcare provider for specific guidance on what to do. If the next dose is approaching, skip the missed dose and resume your regular schedule. Do not double the dose to make up for the missed dose, as this could increase the risk of side effects. It is important to follow the prescribed treatment plan to ensure the effectiveness of the antibiotic. Always consult your healthcare provider if you are unsure about how to proceed with missed doses.
-
How To Use
Cefotaxime 1G injection typically, it should be administered intravenously or intramuscularly, depending on your healthcare provider’s instructions. The injection should be given by a trained healthcare professional in a medical setting.
-
When Not to Use
Following are the situations when Cefotaxime 1G injection should not be used:
- Should not be used in individuals with a known allergy to cefotaxime or other cephalosporins.
- Contraindicated in patients with a history of severe hypersensitivity (anaphylactic reactions) to penicillins or other beta-lactam antibiotics.
- Should not be used in newborns (less than 28 days old) with hyperbilirubinemia, as cefotaxime can displace bilirubin from albumin, leading to an increased risk of bilirubin-induced brain damage (kernicterus).
- Not recommended in patients with a history of severe gastrointestinal diseases, such as colitis or inflammatory bowel disease, as it may worsen these conditions.
- Contraindicated in patients with a history of blood clotting disorders or those on anticoagulant therapy due to increased bleeding risk.
- Should be avoided in patients with severe renal impairment unless adjusted dosing is carefully monitored.
- Should not be used during pregnancy unless clearly necessary, as it is not recommended in the first trimester unless the benefits outweigh the risks.
- Contraindicated in breastfeeding mothers unless no alternative antibiotic options are available.
-
Side Effects
Side effects of Cefotaxime 1G injection:
- Rash
- Diarrhea
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Headache
- Dizziness
- Fever
- Allergies
- Pain
- Bleeding
-
Precautions & Warnings
Following are the precautions and warnings for Cefotaxime 1G injection:
- Use with caution in patients with a history of hypersensitivity or allergic reactions to cephalosporins, penicillins, or other beta-lactam antibiotics due to the risk of cross-reactivity.
- Caution is advised in patients with renal or hepatic impairment as dosage adjustments may be necessary to avoid toxicity.
- Prolonged use may lead to superinfections, such as fungal infections or infections caused by resistant organisms.
- Cefotaxime may cause gastrointestinal disturbances, including diarrhea, nausea, and vomiting. In cases of severe diarrhea, especially with blood or mucus, treatment should be stopped and medical advice should be sought.
- Cefotaxime can alter coagulation parameters and may increase the risk of bleeding, especially in patients on anticoagulant therapy. Monitor prothrombin time and INR during treatment.
- Caution should be exercised in patients with a history of gastrointestinal conditions, such as colitis, as it may exacerbate these issues.
- This medication may cause dizziness, headache, or confusion, especially in elderly or critically ill patients, so caution is advised when engaging in activities requiring alertness.
- Cefotaxime should be used during pregnancy only when absolutely necessary and if the potential benefits outweigh the potential risks to the fetus.
- It is excreted in breast milk, so it should be used with caution in breastfeeding mothers.
- If signs of anaphylaxis (e.g., rash, difficulty breathing, swelling) occur, seek emergency medical attention immediately.
- Use with caution in patients with a history of bleeding disorders, as it may affect clotting mechanisms.
-
Drug Interactions
Following are the drug interactions for Cefotaxime 1G injection:
- May enhance the anticoagulant effect of warfarin and other blood thinners, increasing the risk of bleeding.
- Concurrent use with aminoglycoside antibiotics (e.g., gentamicin) may increase the risk of nephrotoxicity.
- Probenecid may decrease the renal excretion of Cefotaxime, potentially increasing its levels in the blood and the risk of side effects.
- The use of Cefotaxime with diuretics such as furosemide may increase the risk of kidney damage, especially in patients with pre-existing renal issues.
- Cefotaxime may reduce the effectiveness of live bacterial vaccines (e.g., typhoid vaccine).
- The use of Cefotaxime with certain antacids may reduce its absorption.
- May interact with oral contraceptives, potentially reducing their effectiveness, so additional contraception methods may be recommended.
- The use of Cefotaxime with cyclosporine may increase the risk of nephrotoxicity.
- Rifampin may decrease the effectiveness of Cefotaxime when used concurrently.
Shipping & Delivery
-
Courier delivery
Our courier will deliver to the specified address
2-3 Days
From $20
-
Warranty 1 year
-
Free 30-Day returns
Description
Customer Reviews
Rated 0 out of 5
0 reviews
Rated 5 out of 5
0
Rated 4 out of 5
0
Rated 3 out of 5
0
Rated 2 out of 5
0
Rated 1 out of 5
0
Be the first to review “Cefotax (1g) 1 Ampoule Injection” Cancel reply









Reviews
Clear filtersThere are no reviews yet.